Low taper, a nuanced investment strategy, offers a compelling blend of risk mitigation and return enhancement, making it a sought-after approach for discerning investors. By gradually reducing the pace of asset purchases, low taper strategies aim to navigate market fluctuations while preserving capital and pursuing growth.
The judicious application of low taper strategies has been instrumental in shaping the investment landscape, providing a roadmap for investors seeking a balance between risk and reward.
Definition of Low Taper
In the context of investing, “low taper” refers to a gradual reduction in the pace of quantitative easing (QE) by a central bank. QE involves the purchase of long-term bonds by the central bank, which increases the money supply and lowers interest rates.
Low taper strategies aim to reduce the risk of inflation and overheating the economy while maintaining accommodative monetary policy. By gradually reducing the pace of QE, central banks can signal their intention to tighten monetary policy without causing a sudden increase in interest rates.
Examples of Low-Taper Strategies
- Reducing the monthly purchase of bonds by a fixed amount.
- Setting a target date for ending QE.
- Linking the pace of QE to specific economic indicators, such as inflation or unemployment.
Benefits of Low Taper
A low-taper strategy offers numerous advantages, including reduced risk and enhanced returns. It helps investors navigate market volatility while preserving capital and maximizing gains.
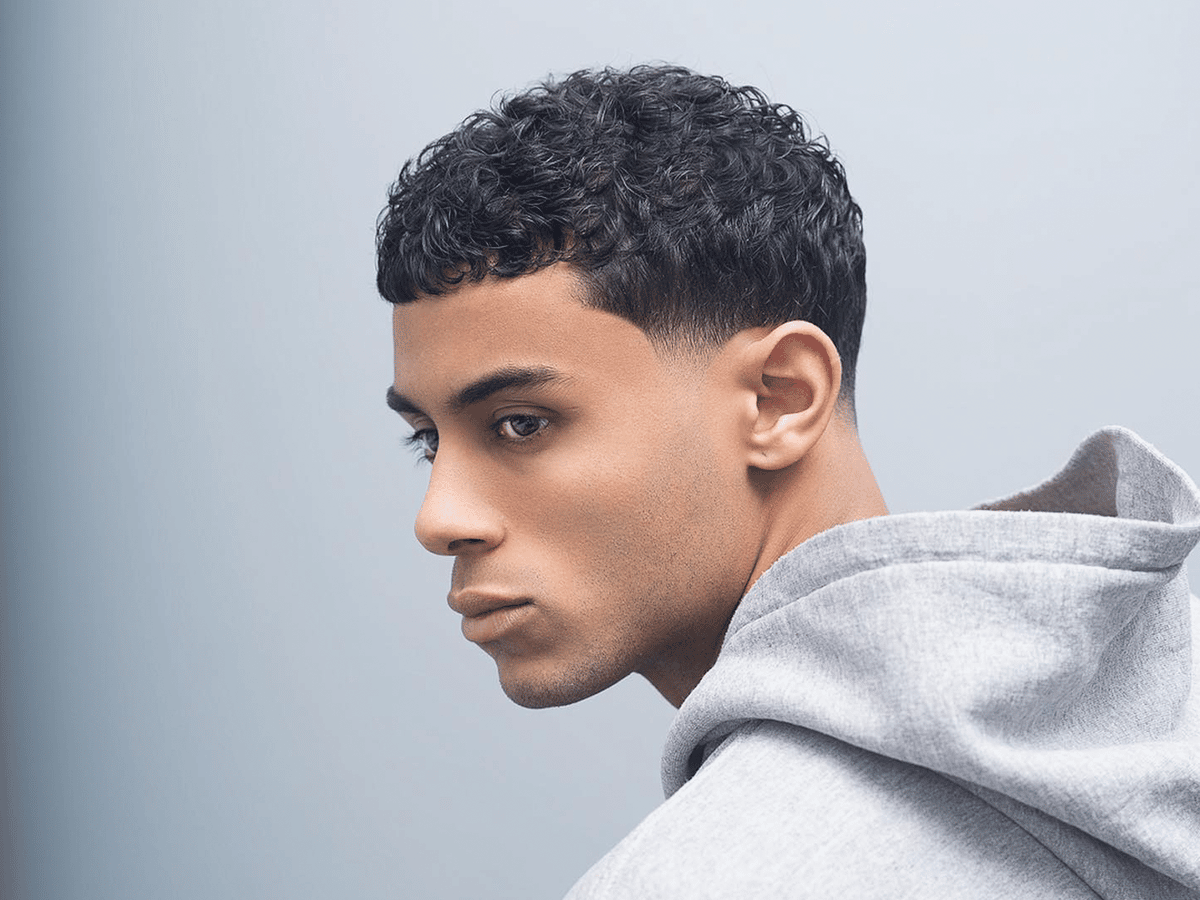
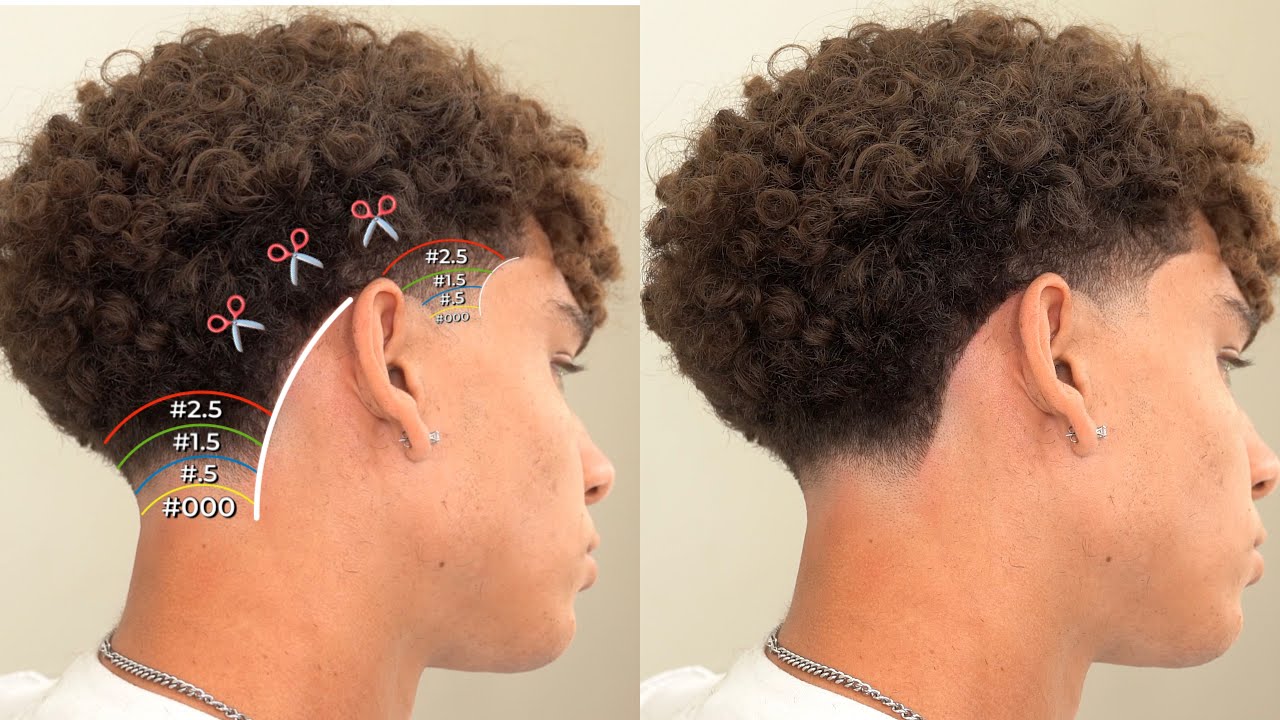
Low taper haircuts are characterized by a gradual transition from short hair at the back and sides to longer hair on top. This versatile style can be customized to suit different face shapes and hair textures, making it a popular choice among men.
To get inspiration for your next low taper cut, check out our gallery of man hair style photos. With so many variations to choose from, you’re sure to find the perfect style for your unique look.
By gradually reducing the taper rate, investors can mitigate potential losses and capitalize on market upswings. This approach provides a more balanced and risk-averse strategy compared to aggressive tapering, which can lead to sharp drawdowns and missed opportunities.
Risk Reduction
- Reduces the impact of market downturns by gradually adjusting the taper rate.
- Preserves capital by limiting exposure to volatile assets during periods of uncertainty.
- Provides a buffer against sudden market corrections, allowing investors to maintain a stable portfolio.
Enhanced Returns, Low taper
- Capitalizes on market recoveries by maintaining exposure to growth-oriented assets.
- Avoids missing out on potential gains by gradually adjusting the taper rate rather than exiting the market abruptly.
- Maximizes returns by balancing risk and reward through a controlled and measured approach.
Risks of Low Taper
While a low-taper strategy can be beneficial in certain circumstances, it also carries potential risks that should be carefully considered.
One of the primary risks associated with a low-taper strategy is the potential for an increase in inflation. If the central bank raises interest rates too slowly, it may not be able to effectively control inflation, leading to a rise in the general price level.
Unexpected Economic Shocks
Another risk of a low-taper strategy is that it may not be suitable in the face of unexpected economic shocks. If the economy experiences a sudden downturn or a negative event, such as a financial crisis, a low-taper strategy may not provide sufficient flexibility to respond effectively.
Comparison with Other Strategies
Low-taper strategies are distinct from other common investment approaches in terms of their underlying principles, risk tolerance, and return expectations.
The following table summarizes the key differences and similarities between low-taper strategies and other common investment approaches:
- Conservative Strategies: Conservative strategies prioritize capital preservation over growth, investing primarily in low-risk assets such as bonds and money market funds. They have lower return potential but also lower risk compared to low-taper strategies.
- Growth Strategies: Growth strategies aim to maximize capital appreciation, investing in high-growth stocks and other assets. They have higher return potential but also higher risk compared to low-taper strategies.
- Balanced Strategies: Balanced strategies seek a balance between growth and preservation, allocating assets across different risk levels. They have moderate return potential and risk compared to low-taper strategies.
Implementation of Low Taper
Implementing a low-taper strategy involves carefully planned steps to gradually reduce the pace of quantitative easing and eventually normalize monetary policy. This process requires a delicate balance between supporting economic growth and maintaining price stability.
The specific steps involved in implementing a low-taper strategy typically include:
- Announcing the Strategy: Central banks typically announce their intention to implement a low-taper strategy well in advance to provide markets with ample time to adjust expectations.
- Gradual Reduction: The central bank gradually reduces the amount of asset purchases it makes each month. This reduction is typically small and incremental to avoid disrupting markets.
- Market Monitoring: Central banks closely monitor market conditions during the tapering process. They assess the impact of the tapering on economic growth, inflation, and financial stability.
- Adjustments: If market conditions warrant, the central bank may adjust the pace or timing of the tapering. This flexibility allows the central bank to respond to unexpected events or changes in the economic outlook.
- Communication: Central banks communicate their decisions and rationale clearly and transparently throughout the tapering process. This helps market participants understand the central bank’s intentions and reduces uncertainty.
Adjusting the Strategy Based on Market Conditions
Central banks may need to adjust their low-taper strategy based on market conditions. If economic growth slows or inflation rises unexpectedly, the central bank may pause or even reverse the tapering process. Conversely, if the economy performs better than expected, the central bank may accelerate the tapering.
The ability to adjust the strategy is crucial to ensure that the low-taper process does not harm economic growth or financial stability. Central banks carefully weigh the risks and benefits of tapering and make decisions based on the best available information.
Case Studies
Low-taper strategies have been implemented in various contexts, with varying degrees of success. Analyzing these case studies can provide valuable insights into the factors that contribute to successful outcomes.
Successful low-taper strategies often involve a gradual and individualized approach, with close monitoring and support from healthcare professionals. Effective communication and patient education are also crucial for ensuring adherence to the plan.
Factors Contributing to Success
- Gradual reduction in dosage over an extended period
- Regular monitoring of symptoms and side effects
- Individualized approach tailored to the patient’s needs
- Strong support from healthcare professionals
- Effective communication and patient education
Factors Contributing to Failure
- Rapid reduction in dosage
- Insufficient monitoring of symptoms and side effects
- Lack of patient adherence to the plan
- Inadequate support from healthcare professionals
- Poor communication and patient education
Future Trends: Low Taper
The future of low-taper strategies is expected to be shaped by technological advancements and changing market dynamics.
One significant trend is the increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in low-taper implementation. These technologies can help automate the process of identifying and managing low-taper trades, making it more efficient and accessible.
Another trend is the growth of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms. DeFi offers the potential to create new low-taper strategies that are not possible within traditional financial systems. For example, DeFi protocols could allow for the creation of synthetic assets that track the performance of low-taper trades, making it easier for investors to access this asset class.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are also expected to impact the implementation of low-taper strategies. For instance, the use of blockchain technology can enhance the security and transparency of low-taper transactions. Additionally, the development of new trading platforms and tools can make it easier for investors to implement low-taper strategies.
Outcome Summary
In the ever-evolving financial realm, low taper strategies continue to hold immense promise. As markets navigate uncharted territories, the ability to adapt and implement tailored low taper approaches will empower investors to harness opportunities while mitigating potential pitfalls. By embracing a holistic understanding of low taper strategies, investors can unlock the gateway to informed decision-making and navigate the complexities of the investment landscape with confidence.